The Cybersecurity Wake-Up Call Your Business Needs: A 2025 Reality Check
Look, We Need to Talk About Your Security
So you're shopping around for a managed service provider, or maybe you're wondering if the IT guy you've had for years is actually keeping you safe. Either way, you're probably losing sleep over questions like: "Are we actually protected?" and "What happens if we get hacked?"
I'm not gonna sugarcoat it—2025 has been brutal for cybersecurity. The average data breach now costs $4.88 million. Yeah, million with an M. And here's the kicker: 68% of breaches happen because someone in your company clicked the wrong thing or used a weak password (Hoxhunt). Not because of some Hollywood-style hacker breaking through your firewall.
I spent the last few weeks going through 14 major security reports and government warnings to put together something actually useful—not the usual sales pitch dressed up as advice. This is what's really happening out there and what you can do about it without needing a PhD in computer science.
The Current Mess We're All Dealing With
Vulnerabilities Are Exploding (And I Mean That Literally)
Get this: in just the first six months of 2025, security researchers found over 21,500 new vulnerabilities. That's 133 new security holes discovered every single day. Every. Single. Day. (DeepStrike).
But here's what keeps me up at night—and what should concern you too: 28% of these vulnerabilities get exploited within 24 hours of being announced. Remember when you could wait a week or two to install updates? Those days are gone. If your IT person is saying "we'll patch next month during our maintenance window," you're already behind.
Ransomware Isn't Going Anywhere
You've probably heard about ransomware attacks in the news. They're not slowing down— 73% of exploited vulnerabilities are being used specifically for ransomware(PKWARE).
Take Qantas Airways. 5.7 million customer records compromised. Or SimonMed Imaging—1.27 million medical records exposed. The thing that gets me about these cases? They weren't sophisticated attacks. Most could've been prevented with basic security hygiene.
Supply Chain Attacks: The Nightmare You Didn't Know You Had
This one's honestly terrifying. There was this attack called "Shai-Hulud" that compromised over 500 npm packages—basically infecting a huge chunk of the JavaScript coding ecosystem. It worked like a digital virus: steal developer credentials, inject malicious code, spread automatically to other packages, and boom—thousands of companies unknowingly deploy infected software (CISA).
Think about that. You're doing everything right on your end, but the software vendor you trust has been compromised. You can't just trust the name on the box anymore.
Phishing Has Gone Completely Insane
Here's a stat that made me do a double-take: phishing has increased 4,151% since ChatGPT came out. Not 415%. Four thousand percent. AI made it ridiculously easy for attackers to create convincing fake emails.
And get this—64% of businesses report Business Email Compromise attacks, with average losses of $150,000 each. That's enough to sink a small business overnight. The most common tricks? Fake Microsoft security alerts, bogus DocuSign documents, and internal HR emails about salary updates (Hoxhunt).
Oh, and 80% of phishing sites now use HTTPS—that little padlock that's supposed to mean "this site is safe." Doesn't mean squat anymore.
Your Employees: The Good News Nobody's Talking About
Training Actually Works (Like, Really Works)
Okay, here's where I get to share something positive for once. Despite all the doom and gloom, employee security training is incredibly effective. I'm talking about real, measurable results.
Researchers analyzed over 50 million phishing simulations and found that companies doing regular security training saw an 86% reduction in successful phishing attacks. Eighty-six percent! (Hoxhunt)
The baseline failure rate—how many people click on fake phishing emails—dropped from 20% down to just 3.2% after consistent training. Even better, after a year of training, 64% of employees actively report suspicious emails instead of just deleting them.
Financial services companies did the best (74% success rate after 12 months), but even healthcare—which has historically struggled—hit 62%. That's with the same employees, same company. Just better training.
But Insider Threats Are Real
Insider threats have jumped 44% since 2020, and the costs keep climbing (InfoSec Hong Kong). Before you start suspecting everyone in your office though, here's the breakdown: 56% of insider incidents are from negligence, not malicious intent. Someone who doesn't realize clicking that link was a bad idea.
Only 26% are actual intentional crimes. Most of your employees aren't trying to steal from you—they just need better training and tools.
Warning signs your IT team should watch for:
- People accessing way more data than their job requires
- System logins at 2 AM when nobody should be working
- Repeated security policy violations
- That disgruntled employee who just got passed over for promotion
What Your MSP Should Actually Be Doing
1. Zero Trust—And No, That's Not Just a Buzzword
The National Institute of Standards and Technology put out comprehensive Zero Trust guidance in June 2025 (NIST SP 1800-35). This should be your MSP's playbook.
Zero Trust is simple in concept: trust nothing and nobody by default. Every access request gets verified, every time. I don't care if you're the CEO logging in from your office computer for the hundredth time today—still gotta verify.
What this looks like in practice:
- Multi-factor authentication on everything (yes, everything)
- Network segmentation so one breach doesn't compromise everything
- Least-privilege access (people only get access to what they absolutely need)
- Continuous monitoring
- Encryption everywhere
Is it annoying sometimes? Sure. But you know what's more annoying? Explaining to customers why their data got stolen.
2. Endpoint Protection That's Not From 2015
Traditional antivirus is basically useless now. Sorry to be blunt, but that McAfee or Norton you installed five years ago? It's checking for threats we already know about. Modern attacks are smarter than that.
Your MSP should be using:
Next-Gen Antivirus (NGAV)
Uses machine learning to spot threats based on behavior, not just signature matching. It can catch brand-new threats that nobody's seen before.
Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR)
Constantly monitors and records everything happening on your computers. When something suspicious happens, it can respond automatically—blocking the threat before it spreads.
Extended Detection and Response (XDR)
This is the full package. It connects the dots across your entire system—computers, network, cloud services, email—and builds a complete picture of an attack (Cynet). Instead of seeing isolated incidents, you see the whole story.
3. Behavioral Analytics: Teaching Computers to Notice When Things Are Weird
One of the coolest developments in 2025 is User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA). It learns what's normal for each person and system, then alerts when something's off.
Like if Bob from accounting suddenly logs in at 3 AM and downloads your entire customer database—that's not normal Bob behavior, and the system would flag it immediately.
Your MSP should monitor for:
- Unusual data access patterns
- Weird login times and locations
- Access to systems someone doesn't normally use
- Abnormal network traffic
- Credential usage that doesn't match normal patterns
The system gets smarter over time, adapting as your business changes (CISOGrid).
4. Fast Patch Management (Because "Eventually" Isn't Good Enough)
Remember how I mentioned 28% of vulnerabilities get exploited within 24 hours? Your patch cycle needs to operate in days, not weeks or months.
Your MSP needs:
- Automated scanning for vulnerabilities
- Smart prioritization (not every patch is equally urgent)
- Virtual patching for systems that can't be updated immediately
- Emergency protocols for critical threats
- Testing procedures so patches don't break stuff (DeepStrike)
And no, "we'll do it next quarter" isn't acceptable anymore.
5. Email Security That Assumes Everyone's Out to Get You
94% of malware comes through email. So yeah, email security is kind of important.
Must-haves:
- DMARC authentication to prevent email spoofing
- Advanced scanning of attachments and links
- Regular phishing simulation training
- Automatic quarantine of suspicious emails
- Warning banners on external emails
- Disabled auto-forwarding to outside addresses (National Cybersecurity Alliance)
6. DDoS Protection
Distributed Denial of Service attacks can knock your website and services offline. Your MSP should have:
- Rate limiting to block traffic floods
- Web Application Firewall (WAF) for sophisticated attacks
- Traffic distribution systems
- Custom filtering based on your specific needs
- Monitoring for attack indicators (Cloudflare)
7. Supply Chain Security (Thanks, Shai-Hulud)
After that npm attack I mentioned earlier, supply chain security can't be ignored anymore.
Your MSP needs to:
- Review all software dependencies
- Pin versions to known-safe releases
- Monitor code repositories
- Harden GitHub security (if you use it)
- Assess vendor security practices
- Segment networks to contain supply chain compromises (CISA)
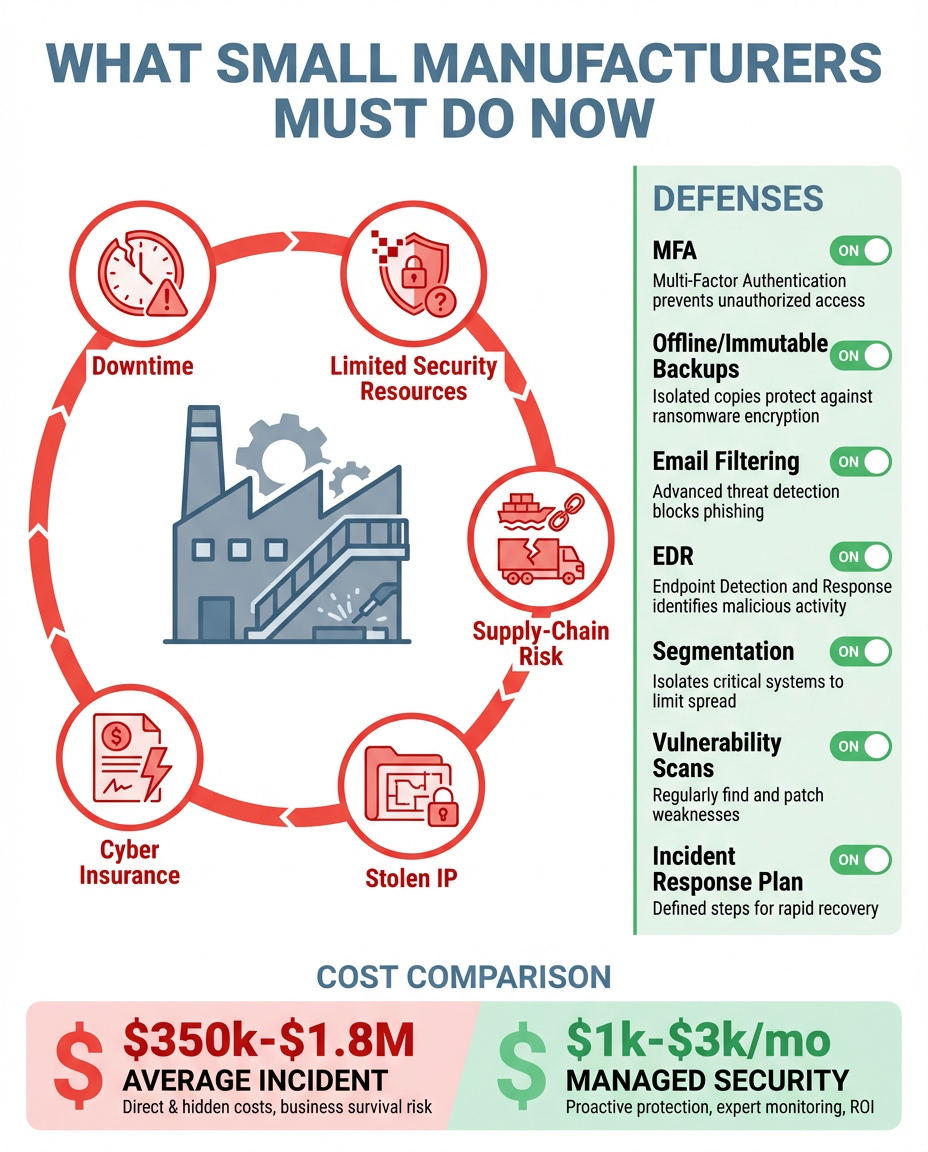
Let's Talk Money (Because You're Thinking About It)
What Security Costs
Real talk: comprehensive managed security for a 50-person company typically runs $3,000-$8,000 per month. Factors that affect price:
- Number of devices and servers
- Compliance requirements (HIPAA, PCI-DSS, etc.)
- 24/7 monitoring or business hours only
- Incident response services included
- Advanced features (SIEM, XDR, penetration testing)
I know that seems like a lot. But let's compare it to the alternative.
What a Breach Costs
- Average data breach: $4.88 million
- Business Email Compromise: $150,000 average loss
- Ransomware: $200,000+ median ransom (plus recovery, downtime, reputation damage)
- Healthcare breaches: $5.9 million average (PKWARE, Hoxhunt, DeepStrike)
Beyond the direct costs:
- Average 21 days of downtime for ransomware
- Customer trust? Gone.
- Regulatory fines
- Legal fees
- Competitive advantage? Lost.
- Business survival: 60% of small businesses close within 6 months of a major cyberattack
Suddenly that monthly security bill doesn't look so bad, does it?
Questions You're Probably Asking
"Do we really need all this? We're just a small business."
Yes. Absolutely yes. Attackers specifically target small businesses because you have less protection. That Qantas breach that affected 5.7 million customers? Came through a third-party vendor (PKWARE). That vendor could be you.
"Can't we just use free antivirus and be careful?"
No. I wish the answer was different, but it's not. Free tools are designed for personal use, not business protection. And "being careful" doesn't work when 28% of vulnerabilities get exploited the same day they're announced (DeepStrike).
"How long does implementation take?"
Typical timeline is 3-6 months with a phased approach:
- Month 1: Assessment, MFA, endpoint protection
- Months 2-3: Email security, network segmentation, monitoring
- Months 4-6: Advanced controls, training programs, policy refinement
But critical stuff (MFA, endpoint protection, email security) should be done within 30 days.
"How do I know if my current MSP is good enough?"
Ask them these questions:
- Do you monitor our systems 24/7?
- How fast do you patch Critical and High severity vulnerabilities?
- Do you implement Zero Trust principles?
- What endpoint technology do you use—NGAV, EDR, or XDR?
- How often do you run phishing training?
- Do you use behavioral analytics?
- What's your incident response process, and when did you last test it?
If they can't give you specific, confident answers with actual technology names and timeframes, start looking elsewhere.
Your Action Plan (Actually Useful Steps)
The 2025 threat landscape is rough, but it's manageable with the right approach. Here's what to do:
This Week:
- Turn on MFA for all business accounts (start with email and financial systems)
- Update all software to current versions
- Hold a quick team meeting about phishing
- Audit who has access to what (remove unnecessary permissions)
This Month:
- Get a comprehensive security assessment
- Grade your current MSP against this guide
- Set up DMARC email authentication
- Start security awareness training
This Quarter:
- Deploy modern endpoint protection (EDR or XDR)
- Segment your network
- Fix your patch management process
- Create and actually test incident response plans
- Begin Zero Trust implementation
Final Thoughts
Cybersecurity in 2025 isn't just about avoiding disasters—it's about being able to operate confidently in a digital world that's increasingly hostile. With proper controls, trained employees, and an MSP partner who actually knows their stuff, you can dramatically reduce your risk.
The stats are scary: 21,500+ vulnerabilities in six months, 4,151% increase in phishing, 86% of incidents involving human error. But here's the counterpoint: proper security and training can reduce incidents by 86%, and catching breaches within 200 days saves an average of $1.2 million compared to slower detection.
Your business deserves protection that matches modern threats. The question isn't whether you can afford comprehensive security—it's whether you can afford not to have it.
And honestly? In 2025, you can't.
Sources
Cloudflare. "What Is a Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) Attack?" Cloudflare Learning Center , 1 Jan. 2025, www.cloudflare.com/en-ca/learning/ddos/what-is-a-ddos-attack/.
CISA. "Widespread Supply Chain Compromise Impacting npm Ecosystem." Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency , 23 Sept. 2025, www.cisa.gov/news-events/alerts/2025/09/23/widespread-supply-chain-compromise-impacting-npm-ecosystem.
CISOGrid. "The Human Factor: Behavioral Analytics as a Cybersecurity Trend in 2025." CISOGrid , 18 Oct. 2025, www.cisogrid.com/the-human-factor-behavioral-analytics-as-a-cybersecurity-trend-in-2025/.
Cynet. "Endpoint Protection: The Basics and 4 Key Technologies." Cynet , 10 Oct. 2025, www.cynet.com/endpoint-protection/endpoint-protection-the-basics-and-4-key-technologies/.
DeepStrike. "Vulnerabilities Statistics 2025: CVE Surge & Exploit Speed." DeepStrike Blog , 8 Oct. 2025, deepstrike.io/blog/vulnerability-statistics-2025.
Hoxhunt. "Phishing Trends Report (Updated for 2025)." Hoxhunt , edited by Eliot Baker and Maxime Cartier, hoxhunt.com/guide/phishing-trends-report.
InfoSec Hong Kong. "InfoSec: Insider Threat." Government of Hong Kong Special Administrative Region , 27 Apr. 2025, www.infosec.gov.hk/en/knowledge-centre/insider-threat.
National Cybersecurity Alliance. "Business Email Compromise: What It Is and How to Prevent It." Stay Safe Online , 21 Apr. 2025, www.staysafeonline.org/articles/business-email-compromise-what-it-is-and-how-to-prevent-it.
NIST NCCoE. "Implementing a Zero Trust Architecture: SP 1800-35." Computer Security Resource Center , 10 June 2025, csrc.nist.gov/news/2025/implementing-a-zero-trust-architecture-sp-1800-35.
PKWARE. "Data Breaches 2025: Biggest Cybersecurity Incidents So Far." PKWARE Blog , 25 Nov. 2025, www.pkware.com/blog/recent-data-breaches.
Yıldız, Okan. "Mastering Advanced Evasion Techniques: An In-Depth Guide." Medium , 3 Dec. 2024, medium.com/@okanyildiz1994/mastering-advanced-evasion-techniques.